Everything You Need to Know About Migraines
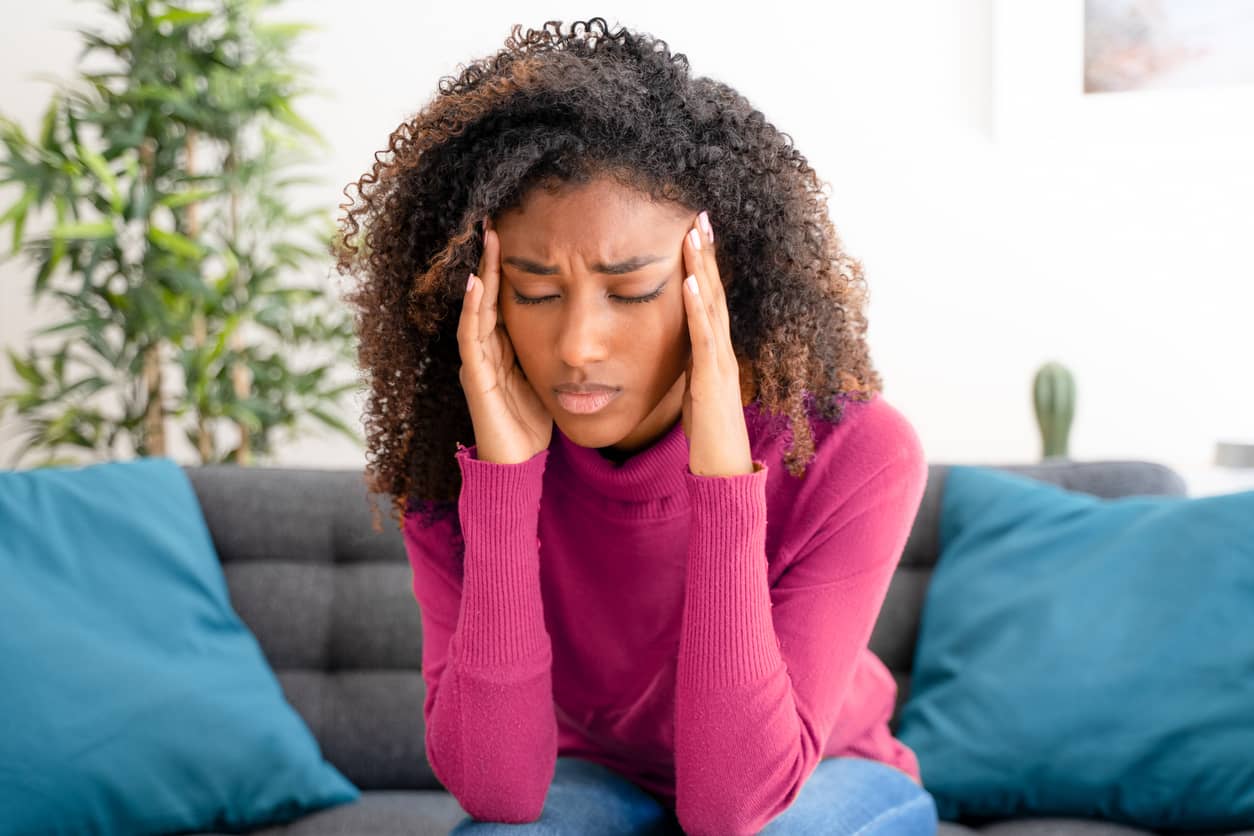

A migraine is a very severe type of headache. They can be severely debilitating and interfere with your everyday life. They often present as severe type throbbing pain on one side of the head, accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and light sensitivity. However, it can affect both sides of the head or even change sides.
Migraine attacks can last from four hours to several days. In 2016, one research study stated that three billion individuals worldwide were estimated to have a migraine or tension-type headache that year. Therefore, migraine is recognized to be one of the most prevalent disorders worldwide.
Migraine Symptoms
The most common symptoms of a migraine include:
- An intense, throbbing, or pounding headache
- Pain usually affects the front or one side of the head
- The throbbing pain is often made worse by movement
- Nausea or vomiting
- Neck stiffness
- Increased sensitivity to light
- Increased sensitivity to smell
- Increased sensitivity to sound
- Poor concentration
- Feeling hot, cold, or sweating
- An increased need to pass urine
- Stomach aches and diarrhea
- Fatigue post migraine - sometimes for several days
The Four Stages of Migraine
There can be four different stages of a migraine, although not everyone who has migraines goes through all the stages. Each stage has different symptoms.
-
Prodrome. This stage is the days leading up to a migraine. Subtle symptoms and changes might begin to happen, such as:
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mood swings
- Problems with reading
- Trouble sleeping, fatigue, and lots of yawning.
- Nausea
- Increased sensitivity to light and sound
- Increased urination
- Fluid retention
- Muscle stiffness
- Food cravings
-
Aura. These are reversible nervous system symptoms, which sometimes occur either before, or during a migraine. They can last up to an hour and include:
- Numbness and tingling in one of the limbs
- Visual disturbances
- Temporary loss of sight
- Weakness on one side of the body
- Difficulty speaking
- Attack. This is when the main symptoms of the migraine occur (like those listed in the symptom section). The attack stage of the migraine can last anything from four hours to a few days.
- Post-drome. The final stage is the days following the migraine. People often find they cannot concentrate, feel confused, and are fatigued. It can also leave you with a depressed or euphoric mood.
Migraine Triggers
Migraine triggers can come in several forms, such as foods, hormonal changes, or medication. The most common reported triggers are:
- Stress
- Skipping meals or dieting
- Certain foods (like chocolate, alcohol, or fermented foods)
- Caffeine
- Certain medications
- Hormonal changes in women around the time of a period, or when going through puberty or the menopause
- Flashing lights
- Weather conditions like storms or changes in weather pressure
- Overexertion
- Dehydration
- Sleep loss
- Loud noises
- Exposure to smoke, perfumes, or other odors
Everyone has different migraine triggers. It helps to keep a diary to learn what your triggers are in the hope of avoiding them.
10 Tips to Help Prevent Migraines
- Learn your triggers. By keeping a migraine diary, you can learn your personal triggers and avoid them where possible.
- Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water to help prevent dehydration which is a known migraine trigger.
- Sleep well. Too little or too much sleep can be a migraine trigger. Getting a regular 7-8 hours a night, with a good sleep hygiene routine, is what to aim for.
- Try yoga. Studies have found that yoga can reduce the frequency of migraine attacks and make them less intense.
- Don't skip meals. It can lead to a drop in blood sugar which can cause a migraine attack.
- Exercise regularly. It can help to prevent migraines, reduce stress, and aid sleep.
- Stop smoking. The nicotine in cigarettes constricts the blood vessels in your brain, which can cause a migraine attack.
- Boost your magnesium. Research shows that magnesium can help prevent migraines.
- Boost your riboflavin. Also known as vitamin B2, studies have shown that riboflavin can reduce migraine frequency.
- Try butterbur. Butterbur appears to reduce the frequency of migraines but can have side effects. Therefore, you should seek medical advice before taking butterbur.
Share
Your share can inspire countless others.